The var, let and const are the keywords basically used in Javascript to declare variables. Among them var is the oldest way of declaring a variable. Other two let and const are introduced in ES2015 (ES6) update. Nowadays let and const are used more frequently in modern javascript compared to var.
In this article, we will try to understand the difference between them in respect to their scope.
Before getting into the difference first we need to know what is function scope and block scope.
Function Scope – Created by declaring a function
Block Scope – Created by if statement, for loops, while loops etc.
var in Javascript:
Var declarations are globally or functionally scoped. The var is globally scoped when it is declared outside a function and it is available for the whole program. Var is functionally scoped when it is declared inside a function.
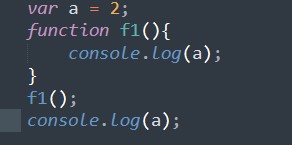
Example of var with global scope:
Output:
2
2
The scope of variable a is global and it can be accessed anywhere in the program.
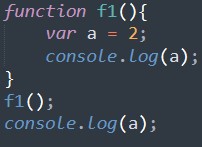
Example of var with function scope:
Output:
2
Reference Error: a is not defined
The scope of variable is within the function so if we try to access outside the function it shows error.
Limitation with var:
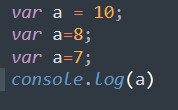
Var variable can be redeclared and updated. If we accidentally declared a new variable with the same name, it will override the existing value of that variable.
Output:
7
Last assigned value 7 is updated to the variable a.
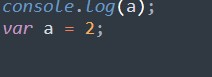
If we use the var variable before declaration it is initialized with undefined value.
Output:
Undefined.
Let in javascript:
It is an improved version of var keyword. Let does not allow variable redeclaration.
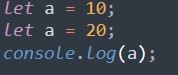
Output:
Syntax error: Identifier ‘a’ has already been declared.
Scope of let:
Let is block scoped.
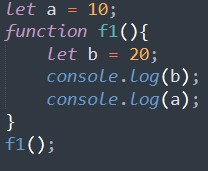
Output:
20
10
Now try to access b outside the function.
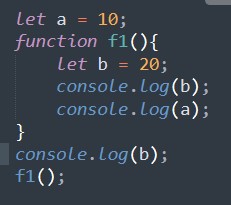
Output:
Reference Error : b is not defined.
If we use a variable before declaration it is not initialized with undefined just returns an error.
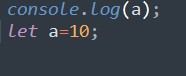
Output:
Reference Error: Cannot access ‘a’ before initialization
const in javascript:
Const variables maintain constant values. They share some similarities with let.
Like let declarations, const are block scoped. The difference is that unlike let, const cannot be updated or re-declared.
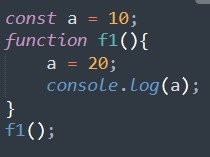
Output:
Type Error: Assignment to constant variable
User cannot change the properties of const object but they can change the value of properties of const object.
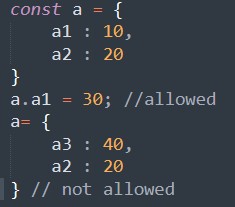
Output:
Type Error : Assignment to const variable.
Points to remember
| var | let | const |
| Function scoped | Block scoped | Block scoped |
| Allow duplicate identifiers | Does not allow duplicate identifiers | Does not allow duplicate identifiers |
| Value can be updated | Value can be updated | Value cannot be updated |
| Hoisted and initialized with undefined | Hoisted but error if we try to access before declaration | Hoisted but error if we try to access before declaration |