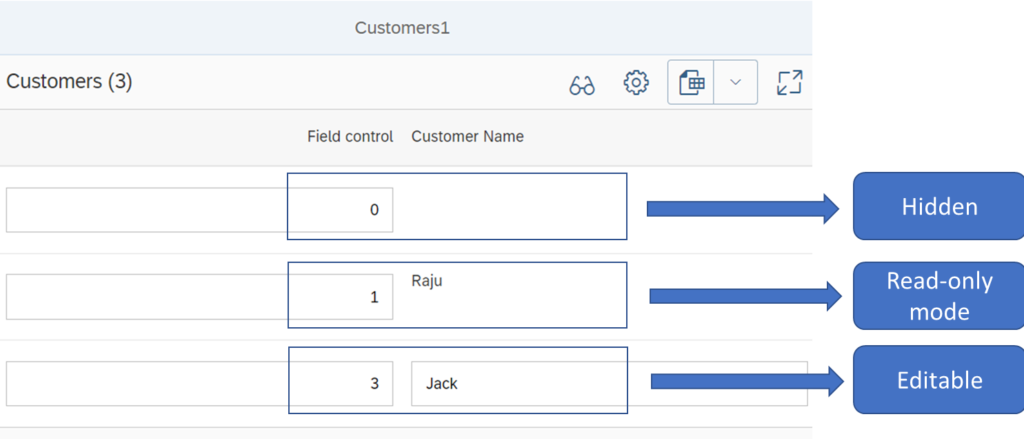
Sap dynamic field-control annotation is used to dynamically change the behaviour of the UI. The metadata generated is used to interpret and change the state of the UI control to visible,editable etc.
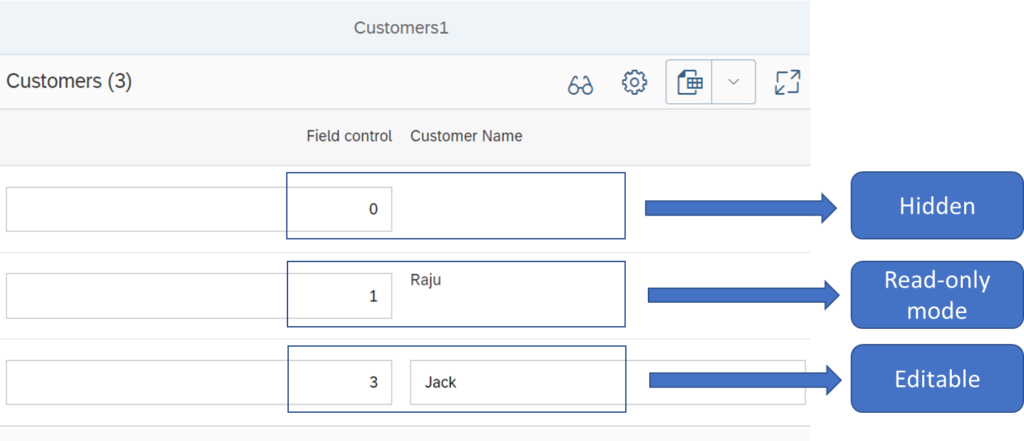
The following needs to be defined in order to use field control annotations
- Usage of smartfield must be mentioned in Smart Table
- Field control annotations must be present in the metadata file
- Appropriate field control values must be sent in the http response.
Smartfield in Smart Table
<core:View xmlns:core="sap.ui.core" controllerName="initialView.controller"
xmlns="sap.m"
xmlns:smart="sap.ui.comp.smarttable"
xmlns:customData="http://schemas.sap.com/sapui5/extension/sap.ui.core.CustomData/1"
height="100%">
<Page id="page1" title="Customers1">
<VBox fitContainer="true">
<smart:SmartTable id="smartTable1"
entitySet="CustomerSet"
tableType="ResponsiveTable"
showFullScreenButton="true"
header="Customers"
showRowCount="true"
editTogglable="true"
customData:useSmartField="true"
useTablePersonalisation="true"
initiallyVisibleFields="FC,Name"
enableAutoBinding="true">
</smart:SmartTable>
</VBox>
</Page>
</core:View>
Field control annotations in Metadata file
<EntityType Name="CustomerType"
sap:label="Customers"
sap:content-version="1">
<Key>
<PropertyRef Name="Id" />
</Key>
<Property Name="Id"
Type="Edm.String"
Nullable="false"
MaxLength="10"
sap:visible="false"
sap:label="Customer ID"
sap:creatable="false" />
<Property Name="FC"
Type="Edm.Byte"
sap:label="Field control" />
<Property Name="Name"
Type="Edm.String"
MaxLength="70"
sap:field-control="FC"
sap:creatable="false"
sap:updatable="true"
sap:label="Customer Name" />
</EntityType>
<EntityContainer Name="CustomerNamespace_Entities"
m:IsDefaultEntityContainer="true"
sap:supported-formats="atom json xlsx">
<EntitySet Name="CustomerSet"
EntityType="CustomerNamespace.CustomerType"
sap:creatable="false"
sap:updatable="true"
sap:deletable="true"
sap:content-version="1" />
</EntityContainer>
As seen in the above metadata, the following conditions must be met.
- The Entityset must have annotation sap:updatable=”true” set at the global Entityset level
- The main property ( as in above example “Name”) must have the annotation sap:field-control=”FC” and sap:updatable=”true”
- The field control property must also be present ( Property Name=”FC” )
The backend must send the appropriate Field control values in the http Response.
{“d”: {
“__count”: “2”,
“results”: [
{
“__metadata”: {
“id”: “Customer_Odata_Service.CustomerSet/CustomerSet(‘1000’)”,
“uri”: “Customer_Odata_Service.CustomerSet/CustomerSet(‘1000’)”,
“type”: “CustomerNamespace.CustomerType”
},
“Id”: “1000”,
“Name”: “Mani”,
“FC”: 0
},
{
“__metadata”: {
“id”: “Customer_Odata_Service.CustomerSet/CustomerSet(‘1001’)”,
“uri”: “Customer_Odata_Service.CustomerSet/CustomerSet(‘1001’)”,
“type”: “CustomerNamespace.CustomerType”
},
“Id”: “1001”,
“Name”: “Raju”,
“FC”: 1
},
{
“__metadata”: {
“id”: “Customer_Odata_Service.CustomerSet/CustomerSet(‘1002’)”,
“uri”: “Customer_Odata_Service.CustomerSet/CustomerSet(‘1002’)”,
“type”: “CustomerNamespace.CustomerType”
},
“Id”: “1002”,
“Name”: “Jack”,
“FC”: 3
}
]
}
}
As seen in the above http response, the field control contains values such as 0 for hidden, 1 for read only, 3 for editable. This is also seen in the Smart table output picture shown in this post beginning.