numpy.tril() returns a copy of the array matrix with an element of the lower part of the triangle with respect to k. It returns a copy of array with lower part of triangle and above the kth diagonal zeroed.
Syntax:
numpy.tril(m,k=0)
Parameters:
m- number of rows in the array.
k-It is optional. Diagonal below which to zero elements. k=0 is the main diagonal and its default.
k>0 is above it and k<0 is below it.
Return value:
It returns a copy of the matrix with elements above the kth diagonal zeroed.
Example:
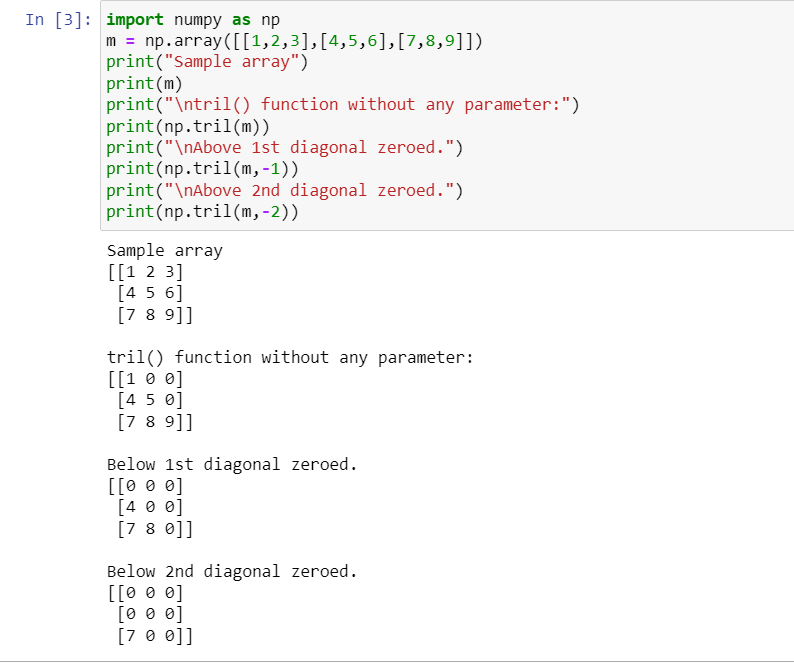
import numpy as np
m = np.array([[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]])
print(“Sample array”)
print(m)
print(“\ntril() function without any parameter:”)
print(np.tril(m))
print(“\nAbove 1st diagonal zeroed.”)
print(np.tril(m,-1))
print(“\nAbove 2nd diagonal zeroed.”)
print(np.tril(m,-2))