In this article, we will discourse on organizational level Analytics, Data Science, and its use cases in the corporate world, Machine Learning and its types and use cases, Deep Learning and how does it work.
What is Analytics
Analytics is the study of data, collected from various sources, to gain insights into a problem.
Types of Analytics

What is Data Science?
Data science uses a mix of tools, robust programming instructions, and principles of machine
learning to process large amounts of unstructured and semi-structured data, to:
- Identify Patterns from the Collected Data Sets.
- Identify the Occurrence of a Particular Event in the Future.

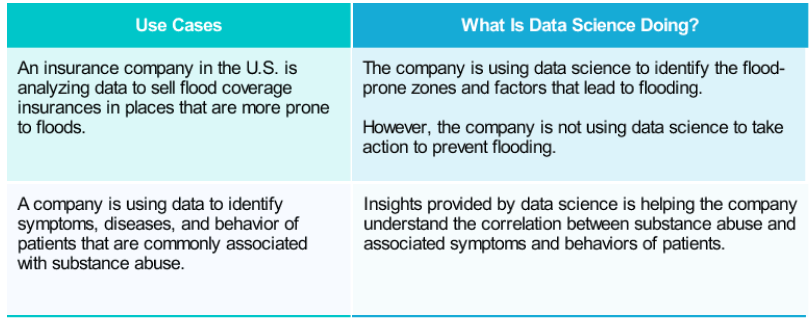
Data Science Use Cases.
Let us look at a few examples of how data science is providing valuable insights to organizations.
What Is Machine Learning?

Machine learning (ML) takes off from where data science ends. While data science relies completely
on programming instructions to detect patterns, ML is adaptive in nature. It gives computer systems
the ability to learn and make predictions by processing data and experiences.
Types of Analytics Used by Machine Learning
ML mainly uses predictive analytics.
Given here are a few key features of predictive analytics.

Machine Learning Use Cases
Let us look at a few examples of how ML algorithms are using insights provided by data science to
make predictions.

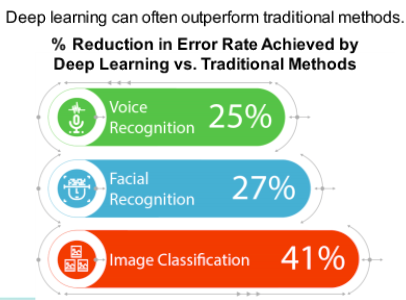
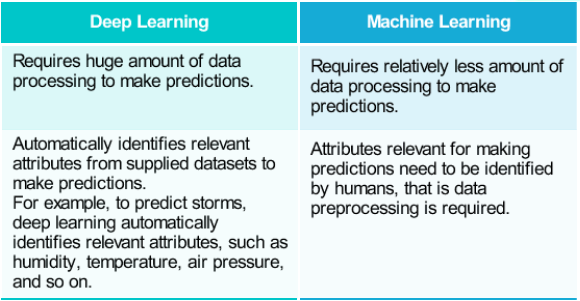
What Is Deep Learning?
Deep learning is an advanced form of ML. It processes a huge amount of data, collected from a wider
range of data sources, and requires very fewer data preprocessing by humans.
How Does Deep Learning Work?
Deep learning uses interconnected layers of software-based calculators, known as “neurons.”
Together, the “neurons” form a neural network, which can ingest a vast amount of data and processes
them through multiple layers. Each layer learns something about the complex features of the data.
Finally, the network makes a determination about that data, assesses whether the determination is correct,
and applies what it has learned to make determinations about new data.

For example, once a neural network learns what an object looks like, it can identify that object in a new image.
In this article, you have learned that:
- Analytics is the study of data, collected from various sources, to gain insights into a problem.
- Data Science gives organizations insights into business problems by processing semi-structured and unstructured data.
- ML algorithms use insights provided by data science to make predictions about future events.