In this article we are going to see about ABAP Dictionary. The data is administered centrally in the SAP system using the ABAP Dictionary. The transaction for the ABAP Dictionary is SE11. The following ABAP Dictionary objects are involved in SE11 transaction.
- Domain
- Data Element
- Structure
- Table type
- Database table
- Type groups
- Views
- Search help
- Block Concept
Now the ABAP Dictionary concepts are explained with list of groceries example.
- Create a Domain
- Create a Data Element
- Create Structure
- Create Data Table
I want to manage and administer the groceries list. Therefore I want to create a data table which stores the list of groceries.
Here are the frequently used items in my grocery list.
- Bread
- Butter
- Honey
- Rice
- Eggs
- Chicken
- Tomato
- Onion
- Olive oil
- Pepper
- Milk
- Coffee
- Plant based milk
- Tomato Bio
- Chicken Nuggets
I listed these items in a table and figured out that the names are not unique. For example 7 and 14 are tomato. But they are of different type. Similarly 6 and 15 are of type chicken, 11 and 13 are of type milk. In order to make the items unique, I want to give a unique no to each grocery item. Say I start with 1000,1001,…. So for Bread, Item Id is 1000. Now comes the question , how many packets of Bread do I buy in a week or during a single purchase. The items onion, rice etc. are measured in kilograms. The item such as milk are measured in litre etc.
We have now identified the data in the groceries list. For example,
Item Id –>1000
Name of Item –>Bread
Size of Purchase –>2 Packets
Unit of Purchase –> Packets
Now let’s have a short look at Data types in ABAP Dictionary. The frequently used data types in ABAP are CHAR,NUMC,DEC,INT1,INT2 and INT4.
The figure shows how different data can be defined using different data types.
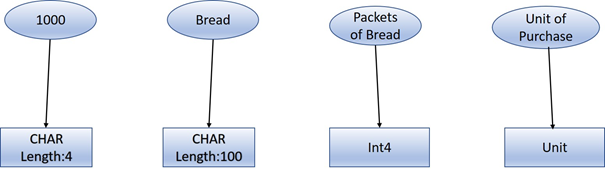
Domain:
Let us create four different domains.
Item Id => ZDOM_Item_Id=>CHAR (Length=4)
Name of Item=> ZDOM_Item_Name=>CHAR(Length=100)
No.of Items=> ZDOM_No_Items=>Int4
Unit of Purchase=>ZDOM_Unit=>UNIT
Data Element:
The Data Element depicts the column name or the field name. So create four different data elements from the respective domains.
Item Id => ZDE_Item_Id=>ZDO_Item_Id
Name of Item=> ZDE_Item_Name=>ZDO_Item_Name
No.of Items=> ZDE_No_Items=>ZDO_No_Items
Unit of Purchase=>ZDE_Unit_of_Purchase=> ZDO_Unit_of_Purchase
In the field description of the data element give a meaningful name. This text appears in the user interface. The text must also be translated into respective language, if the application is maintained in different languages.
Data Table:
Finally, we arrive to the Data table creation section. The fields are defined in the data table with corresponding data elements.
ZDT_ITEM_LIST
| Field Name | Data Elements |
| Item_Id | ZDE_Item_Id |
| Name_of_Item | ZDE_Item_Name |
| No. of Items | ZDE_No_Items |
| Unit_of_Purchase | ZDE_Unit_of_Purchase |
Structure:
The items in the list can be structured using structures in ABAP.
So let’s create a structure
ZST_ITEM_LIST
| Structure Fields | Data Elements |
| Item_Id | ZDE_Item_Id |
| Name_of_Item | ZDE_Item_Name |
| No. of Items | ZDE_No_Items |
| Unit_of_Purchase | ZDE_Unit_of_Purchase |
It is clearly evident, that the structure and Data table may look similar in construction. For Beginners, this will always be a confusion. One of the key difference between Data tables and structures is that a structure will always hold a single line of record. But whereas a Data table will hold a series of records. Below is the pictorial representation.
DATA TABLE
| Item Id | Name of Item | No. of Items | Unit of Purchase |
| 1000 | Bread | 2 | Packets |
| 1001 | Rice | 2 | Kg |
| 1002 | Onion | 1,5 | Kg |
Structure => 1000, Bread, 2, Packets (Single Line of Record)
Table Type:
A table type can be defined from the structure. In order to achieve that, simply define a line type as the structure
ZTable type_Items => Line Type–>ZST_Item_List
This is how data can be managed and maintained in a data table. ABAP provides a structured way of managing the data in data tables using the Development objects such as Domain, Data Element, Structures and Data tables.
References:
SAP ABAP OBJECTS by Felix Roth