Today we will implement linked list data structure in javascript. LinkedList is a dynamic data structure as it can add or remove elements easily.We have already seen about the brief introduction of linked list in previous article.
Linked list implementation:
LinkedList is made of nodes. Each element in a linkedlist is a node which contains a value and a pointer to next node. Each linked list consists of head, tail and length properties. Tail node points to null.
Node creation:
A node contains two items: value and the pointer to next node.
class Node{
constructor(value)
{
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
In the above code a class named node having two properties: element, next is defined. Element holds value of the node and next holds the pointer to next node. Here it is initialized to null.
Now let’s jump into linked list implementation.
Linked List creation:
class LinkedList{
//Creates a linkedlist with passed value.
constructor(value){
//Creates a head node
this.head = {
value: value,
next : null
};
//As there is only one element in the list, head is also a tail
this.tail = this.head;
//Length would be 1
this.length = 1;
}
}
Here a linked list class with a constructor is defined. Head node is initialized to null as there is one node in linked list.
To create an instance of linked list class:
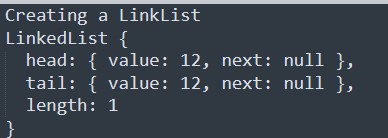
console.log('Creating a LinkList');
const myLinkedList = new LinkedList(12);
console.log(myLinkedList);Creates a Linked list with a value 12. As only one node is created head and tail are same nodes with value 12.
Output:
Print a Linked list:
This method is useful in printing a linked list.
printList(){
//Creates an empty array.
let printArrayList = [];
//Pointer which points to the head node
let currentNode = this.head;
//Start iterating from the first node till you reach the last node
while(currentNode !== null){
//Add every node's value to the array
printArrayList.push(currentNode.value);
//Point pointer to the next node
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
//Return the array
return printArrayList.join(' -> ');
}Add a new tail node using append()
We have seen about creating a node in a linked list. Now we will see about append() function. Every appended node becomes the new tail node.
append(value){
//Create a new Node by creating a instance of a Node class
const newNode = new Node(value);
// Check if head is present or not, if head is empty creates a head
if (this.head == null){
this.head = node;
}
else{ //Else creates a tail
//We need to point current tail's next to the newNode
this.tail.next = newNode;
//Now make newNode a tail node
this.tail = newNode;
//Increase the length by 1
this.length++;
}
return this;
}
Now let’s try to append two nodes with value 22 and 26
console.log('Append Nodes with values 22 and 26:');
myLinkedList.append(22).append(26);
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());How to add a new node in front of the linked list as head?
Answer is prepend() . To add a new head node we will move the current head node one position forward.
//Add the node as a head of the linkedlist
prepend(value){
//Create a new Node by creating a instance of a Node class
const newNode = new Node(value);
//Points this node's next to the head
newNode.next = this.head;
//Now make this node a head node
this.head = newNode;
//Increase the length by 1
this.length++;
return this;
}
Prepend a node with value 6
console.log('Prepend Node with value 6:');
myLinkedList.prepend(6);
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
Insert a node at a given index:
To insert a node at a given index we have to traverse through the list to the previous node and split the list into 2 parts. First merge the right side of list with the node and then assign left using pointer.
//Insertes a node at specified index, say we want to insert 18 at index 2
//Current list: 6 -> 12 -> 22 -> 26
insert(index, value){
//Create a new Node by creating a instance of a Node class
const newNode = new Node(value);
//Counter to loop
let count = 1;
//Create a temp node to traverse through list, which will start from the head node
//Pointing to 6
let previousNode = this.head;
//Traverse the list one node before the specified index, which is previous node
while(count < index){
//Point previous node to next for iterating
previousNode = previousNode.next;
//Increase the count to compare it with index;
count++;
}
//When the loop ends you will be able to have a previous node. Which is 12 in this example.
//First, points new node's next to the previous node's next, so it can hold the list ahead of its index
//New node = 18, So new node will be 18 -> 22 -> 26
newNode.next = previousNode.next;
//Now just point previous node's next to new node.
//Merge left side of the list, 6 -> 12 -> 18 -> 22 -> 26
previousNode.next = newNode;
return this;
}
Let’s insert two node with value 18 at index 2 and value value 9 at index 1:
console.log('Inserting Node at index 2 with value : 18');
myLinkedList.insert(2,18);
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log('Inserting at index 1: 9');
myLinkedList.insert(1,9);
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log('');
Delete method:
It can be performed at 4 places
- Delete head
- Delete tail
- Delete at index
- Delete at node with value
Delete head:
It’s quite simple just delete the head and make the next element as new head.
deleteHead(){
this.head = this.head.next;
this.length--;
return this;
}
Now let’s delete the head node with value 6 and make the node with value 9 as new head
console.log('Deleting Head-Node with value 6:');
myLinkedList.deleteHead();
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log('');Delete Tail:
Traverse to the second last node of the list and points its next pointer to null.
deleteTail(){
let secondLastNode = this.head;
while(secondLastNode.next.next !== null){
secondLastNode = secondLastNode.next;
}
secondLastNode.next = null;
this.length--;
return this;
}
Deleting a tail node with value 26 and making node with value 22 as new tail
console.log('Deleting Tail-Node with value 26');
myLinkedList.deleteTail();
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log('');
Delete a node by index:
First we need to check whether the deleting node is head or not. Then traverse to the previous node and point its next to next.next.
deleteAtIndex(index){
//Check if index is head
if(index === 0){
//Appoint head to the next element
this.head = this.head.next;
this.length--;
return this;
}
let count = 1;
let previousNode = this.head;
while(count < index){
previousNode = previousNode.next;
count++;
}
previousNode.next = previousNode.next.next;
this.length--;
return this;
}
Now let us delete the node at index 2 with value 18
console.log('Deleting Node at index 2 with value 18:');
myLinkedList.deleteAtIndex(2);
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log('');
Delete a node by value:
Here we need 2 pointers. One to traverse the list and the other to point the previous node.
deleteNodeByValue(value){
//Current node to loop through the list
let currentNode = this.head;
//Previous node to update its pointer to next.next node
let previousNode = null;
while(currentNode != null){
//Check if we find the value we are looking for
if(currentNode.value === value){
//Check if it is a head or not by comparing previous node with null
if (previousNode === null) {
//If it is head, then update head to nextnode
this.head = currentNode.next;
}
else{
//If it is not head then simply update previous node
previousNode.next = currentNode.next;
}
//Reduce length by 1
this.length--;
}
//Previous node will point to this node with every iteration
previousNode = currentNode;
//Current node will point to next node for iteration
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return this;
}
We will delete the node with value 22
console.log('Deleting Node with value 22:');
myLinkedList.deleteNodeByValue(22);
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log('');
By now we have seen about creation, insertion, append, prepend, deletion of linked list.
Let’s jump into searching
Search a linked list:
Traverse through the list, compare the value and return true or false.
searchElement(value){
let currentNode = this.head;
while(currentNode !== null){
if(currentNode.value === value) return true;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return false;
}
Here we will search for two elements 12 and 22 one is in the list and the other is not in the list. So it must return true for 12 and false for 22.
console.log('Searching for value 12:');
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log(myLinkedList.searchElement(12));
console.log('Searching for value 22:');
console.log(myLinkedList.searchElement(22));
Complete Linked List implement Code:
class Node {
constructor(value){
this.value = value,
this.next = null
}
}
class LinkedList{
//Creates a linkedlist with passed value.
constructor(value){
//Creates a head node
this.head = {
value: value,
next : null
};
//As there is only one element in the list, head is also a tail
this.tail = this.head;
//Length would be 1
this.length = 1;
}
append(value){
//Create a new Node by creating a instance of a Node class
const newNode = new Node(value);
// Check if head is present or not, if head is empty creates a head
if (this.head == null){
this.head = node;
}
else{ //Else creates a tail
//We need to point current tail's next to the newNode
this.tail.next = newNode;
//Now make newNode a tail node
this.tail = newNode;
//Increase the length by 1
this.length++;
}
return this;
}
//Add the node as a head of the linkedlist
prepend(value){
//Create a new Node by creating a instance of a Node class
const newNode = new Node(value);
//Points this node's next to the head
newNode.next = this.head;
//Now make this node a head node
this.head = newNode;
//Increase the length by 1
this.length++;
return this;
}
//Insertes a node at specified index, say we want to insert 18 at index 2
//Current list: 6 -> 12 -> 22 -> 26
insert(index, value){
//Create a new Node by creating a instance of a Node class
const newNode = new Node(value);
//Counter to loop
let count = 1;
//Create a temp node to traverse through list, which will start from the head node
//Pointing to 6
let previousNode = this.head;
//Traverse the list one node before the specified index, which is previous node
while(count < index){
//Point previous node to next for iterating
previousNode = previousNode.next;
//Increase the count to compare it with index;
count++;
}
//When the loop ends you will be able to have a previous node. Which is 12 in this example.
//First, points new node's next to the previous node's next, so it can hold the list ahead of its index
//New node = 18, So new node will be 18 -> 22 -> 26
newNode.next = previousNode.next;
//Now just point previous node's next to new node.
//Merge left side of the list, 6 -> 12 -> 18 -> 22 -> 26
previousNode.next = newNode;
return this;
}
deleteHead(){
this.head = this.head.next;
this.length--;
return this;
}
deleteTail(){
let secondLastNode = this.head;
while(secondLastNode.next.next !== null){
secondLastNode = secondLastNode.next;
}
secondLastNode.next = null;
this.length--;
return this;
}
deleteAtIndex(index){
//Check if index is head
if(index === 0){
//Appoint head to the next element
this.head = this.head.next;
this.length--;
return this;
}
let count = 1;
let previousNode = this.head;
while(count < index){
previousNode = previousNode.next;
count++;
}
previousNode.next = previousNode.next.next;
this.length--;
return this;
}
deleteNodeByValue(value){
//Current node to loop through the list
let currentNode = this.head;
//Previous node to update its pointer to next.next node
let previousNode = null;
while(currentNode != null){
//Check if we find the value we are looking for
if(currentNode.value === value){
//Check if it is a head or not by comparing previous node with null
if (previousNode === null) {
//If it is head, then update head to nextnode
this.head = currentNode.next;
}
else{
//If it is not head then simply update previous node
previousNode.next = currentNode.next;
}
//Reduce length by 1
this.length--;
}
//Previous node will point to this node with every iteration
previousNode = currentNode;
//Current node will point to next node for iteration
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return this;
}
searchElement(value){
let currentNode = this.head;
while(currentNode !== null){
if(currentNode.value === value) return true;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return false;
}
printList(){
//Creates an empty array.
let printArrayList = [];
//Pointer which points to the head node
let currentNode = this.head;
//Start iterating from the first node till you reach the last node
while(currentNode !== null){
//Add every node's value to the array
printArrayList.push(currentNode.value);
//Point pointer to the next node
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
//Return the array
return printArrayList.join(' -> ');
}
}
console.log('Creating a LinkList');
const myLinkedList = new LinkedList(12);
console.log(myLinkedList);
console.log('Append Nodes with values 22 and 26:');
myLinkedList.append(22).append(26);
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log('Prepend Node with value 6:');
myLinkedList.prepend(6);
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log('Inserting Node at index 2 with value : 18');
myLinkedList.insert(2,18);
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log('Inserting at index 1: 9');
myLinkedList.insert(1,9);
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log('');
console.log('Deleting Head-Node with value 6:');
myLinkedList.deleteHead();
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log('');
console.log('Deleting Tail-Node with value 26:');
myLinkedList.deleteTail();
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log('');
console.log('Deleting Node at index 2 with value 18:');
myLinkedList.deleteAtIndex(2);
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log('');
console.log('Deleting Node with value 22:');
myLinkedList.deleteNodeByValue(22);
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log('');
console.log('Searching for value 12:');
console.log(myLinkedList.printList());
console.log(myLinkedList.searchElement(12));
console.log('Searching for value 22:');
console.log(myLinkedList.searchElement(22));